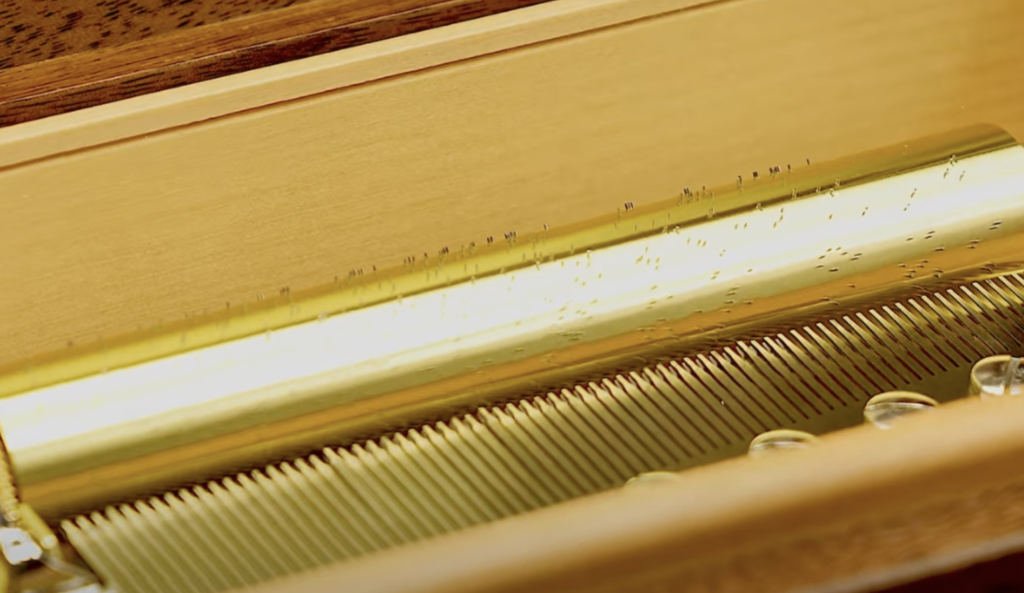

Mechanical Music Movement
The role of the parts of the movement.
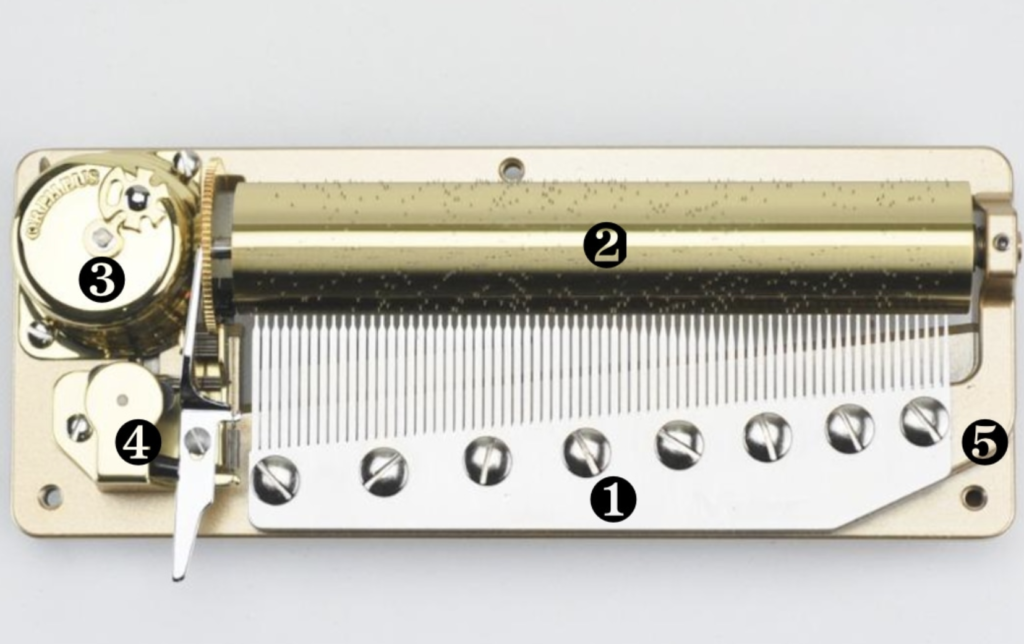
| ❶Comb | While the cylinder and its pins can be likened to the musician’s fingers flying over a keyboard, the comb with its steel teeth is the element that resonates and sings. |
| ❷Cylinder | The cylinder is a brass drum fitted with steel pins that pluck the teeth on the comb’s teeth, playing the notes. A melody consists of multiple notes, each with a specific location on the cylinder. |
| ❸Barrel | The barrel supplies the necessary energy for the movement; it is wound up using a key. |
| ❹Governor | The governor regulates the speed at which the barrel’s spring unwinds, ensuring the cylinder rotates with absolute smoothness for a perfect musical experience. |
| ❺bedplate | The brass bedplate forms the foundation that supports all of the movement’s components. As it also conducts sound frequencies, it enhances the music box’s resonance. |
Cylinder music box Structure
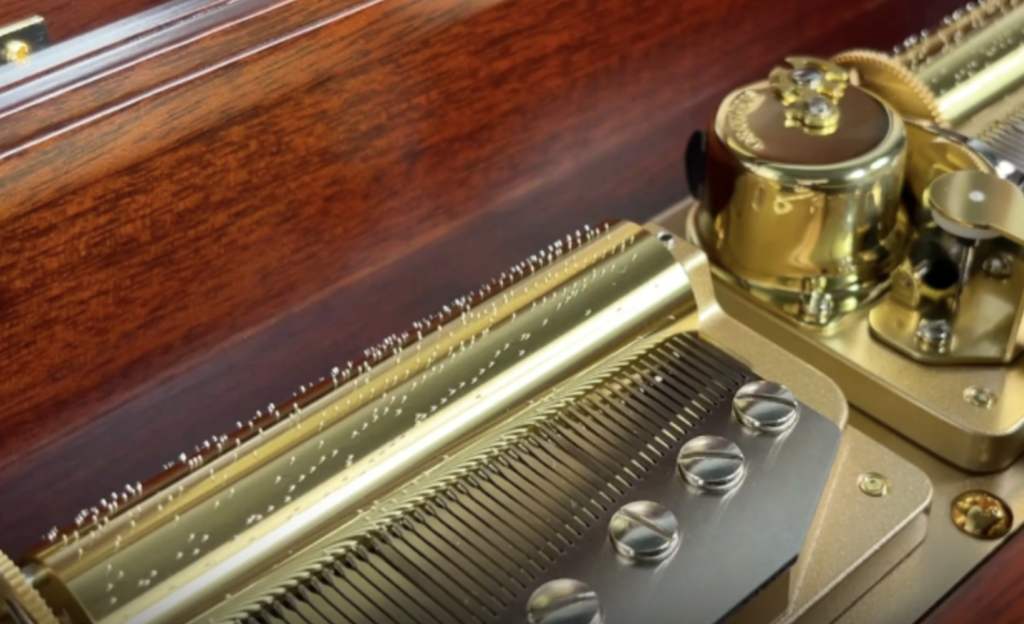

The tunes are recorded on a cylinder with embedded pins.
The cylinder rotates under the force of the mainspring and the pins burst the diaphragm valves to play the melody.
The comb is made of brass (steel material called SKS), with resin inside the cylinder.
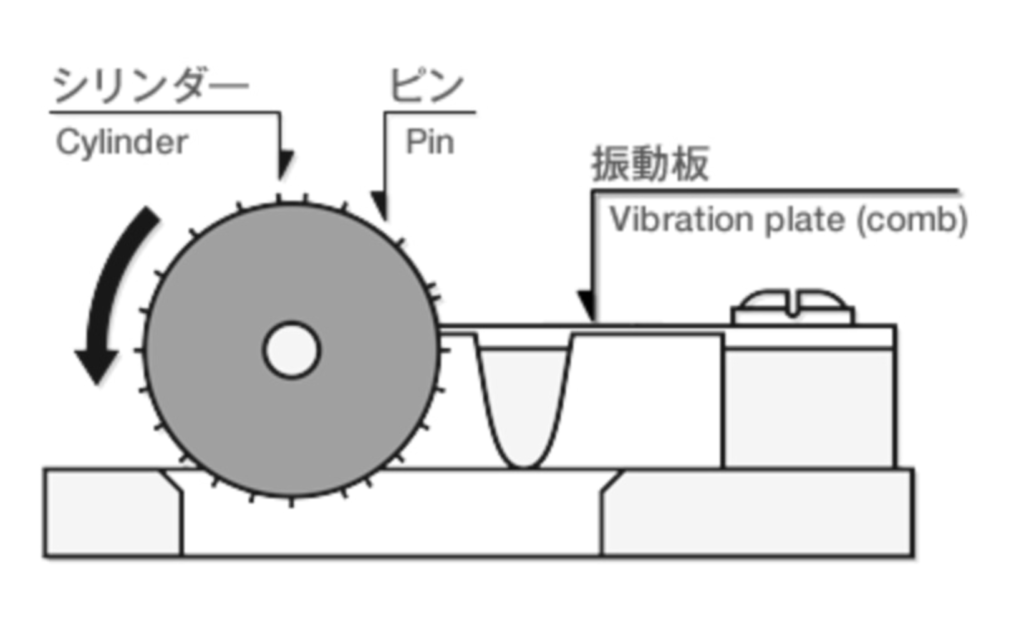
The weight of the resin produces a good sound from the comb. It is the same principle as a pianist using the weight of his hands to produce a soft sound with a core.

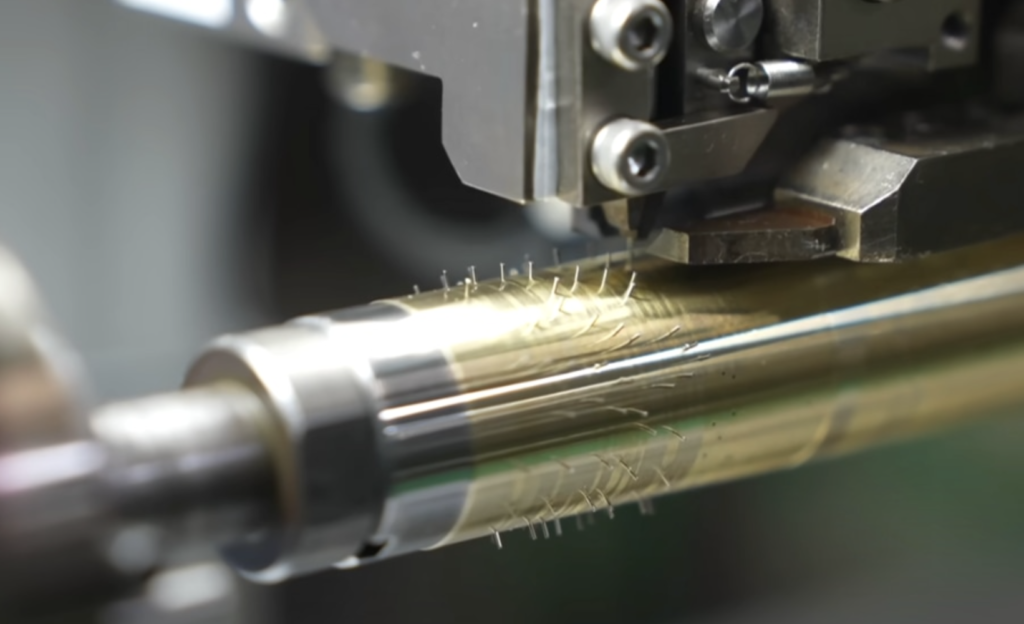
Attaching the pins to the cylinder drum used to be done by hand, but production speed was slow and it was difficult to maintain accuracy and quality.
Today, precision machines are used to drill holes in the cylinders and accurately insert the needles, which has improved the accuracy of reproduction of the original music.

The speed is adjusted by controlling the cylinder’s rotational speed by the frictional force when the rotating disc touches the rubber.
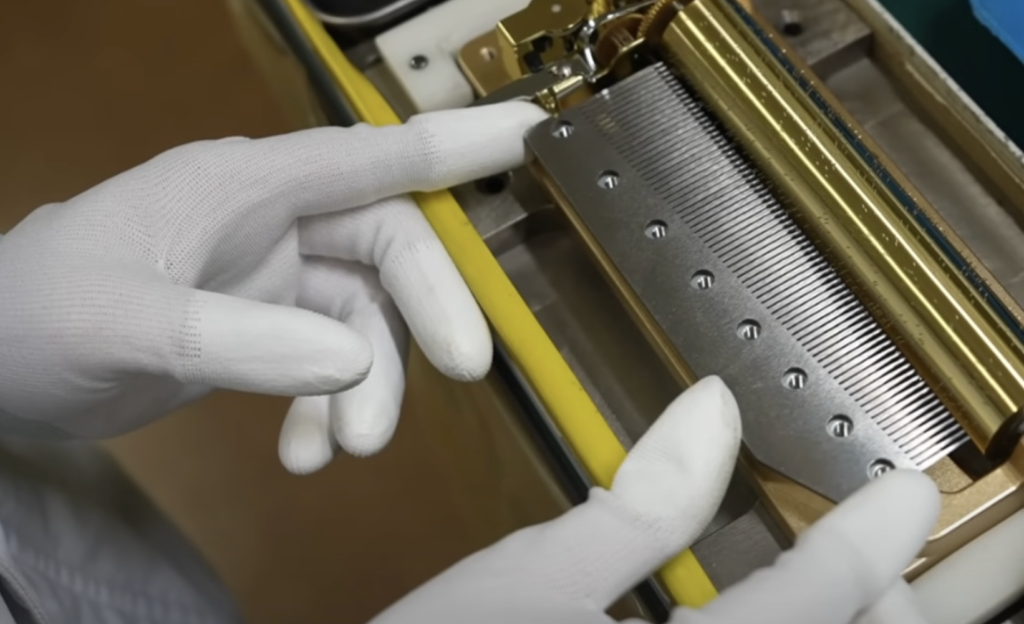

As the rotation speed is determined by the magnitude of the frictional force, the playback speed can be increased or decreased by adjusting the position of the contact.
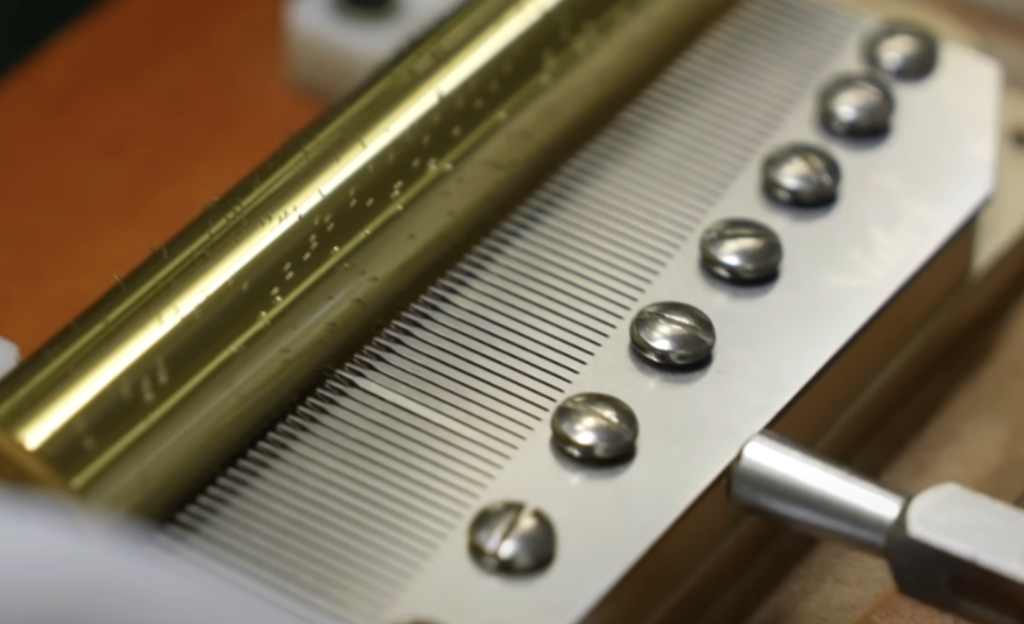

To speed up, the frictional force is reduced and the distance between the rotating plate and the contacting parts is increased, while to slow down, the distance is narrowed to increase the frictional force.
As speed control by the rotary plate is a matter of personal preference, Nidec’s rule of thumb is to adjust the speed to a more generally acceptable rotational speed (30-45 seconds per cylinder revolution). 2-3 second change can make a big difference to the sound.
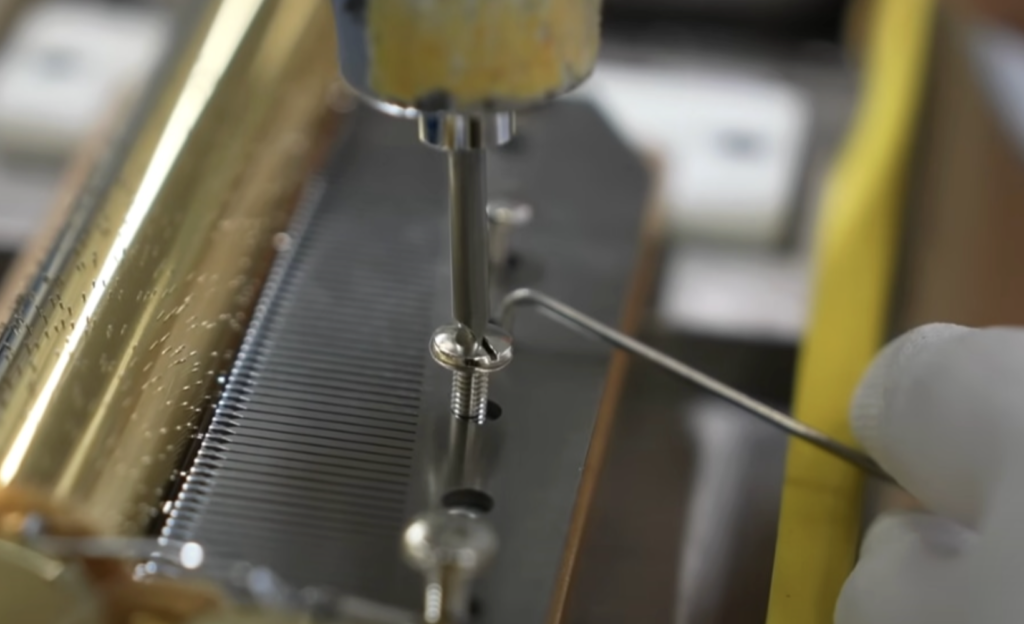

If there are special requests, it is possible to adjust the speed to each customer’s preference, but if it is faster, the load on the gears and the strain on the mechanism increases, and if it is slower, the rotary disc itself wears more, which can easily lead to breakdowns.
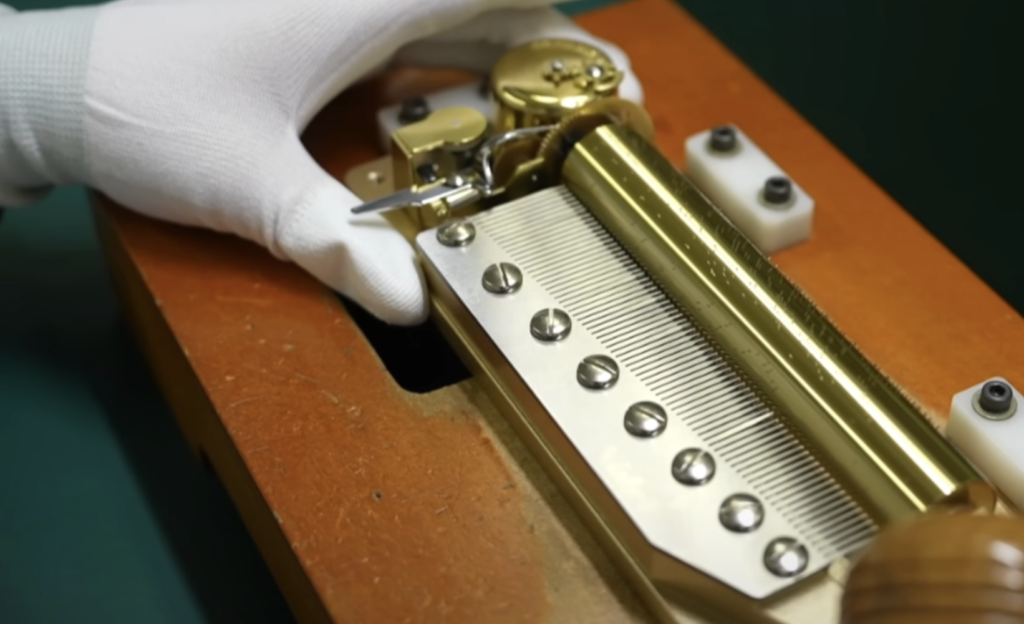

Cylinder music boxes, which look as if they are changing keys to suit the tune, are often presented as an automatic performance device rather than a musical instrument.
The comb teeth are not all neatly aligned in pitch like a keyboard instrument, and the necessary sounds are built into the comb teeth in accordance with the tune and its arrangement.
Therefore, when repairing, the sound cannot be played even if only the cylinder is replaced.
A cylinder music box is only viable when the diaphragm and drum are as a set.
Enjoy Music Box!
